😊 About Me
I am Jiaming Liang. I am a first-year Ph.D student under the supervision of Prof. Hongmin Cai at South China University of Technology. Before this, I completed my Master’s degree at Guangzhou University, and I had the honor of being mentored by Prof. Qiong Wang and Assoc. Prof. Yan Pang
My research interests are primarily focused on medical image analysis and biomedical computing.
🔥 News
- 2025.11.11: 🎉🎉 A paper (MM-UNet) has been accepted for IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM)!!
- 2025.08.25: 🎉🎉 A paper (Slim UNETRV2) has been accepted for IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging!
📝 Publications
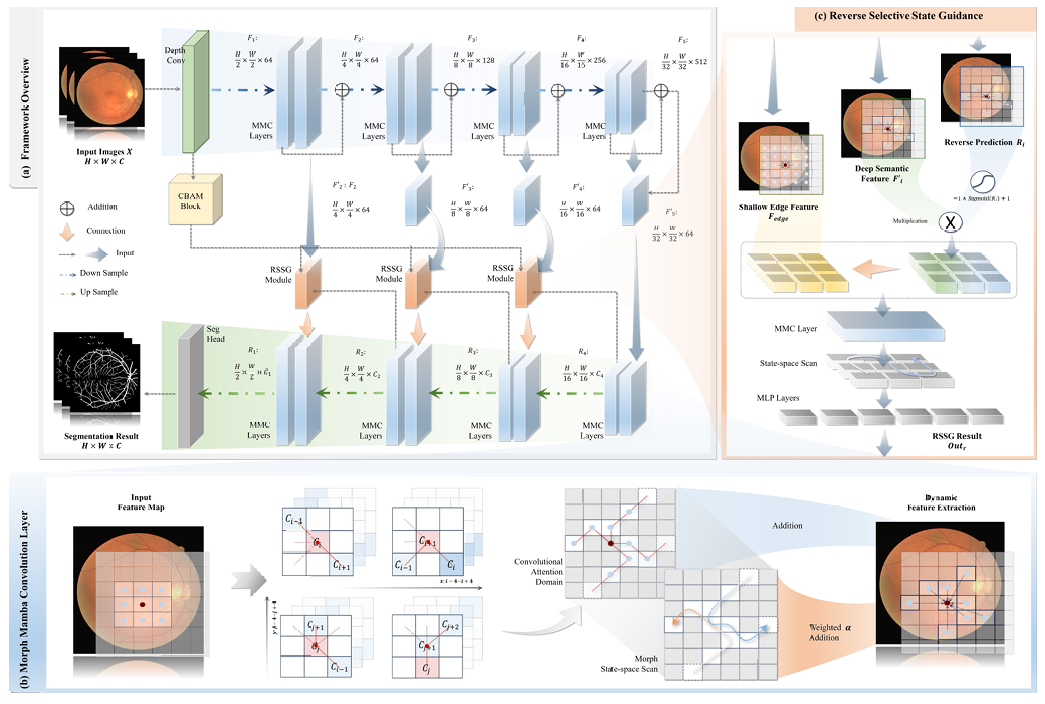
🎉New!!!🎉MM-UNet: Morph Mamba U-shaped Convolutional Networks for Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Jiawen Liu (Co-first author), Yuanbo Zeng (Co-first author), Jiaming Liang (Co-first author), Yizhen Yang, Yiheng Zhang, Enhui Cai, Xiaoqi Sheng, Hongmin Cai*
Project Conference paper (CCF-B)
- This work proposes MM-UNet, a novel architecture tailored for efficient retinal vessel segmentation. The model incorporates Morph Mamba Convolution layers, which replace pointwise convolutions to enhance branching topological perception through morph, state-aware feature sampling.
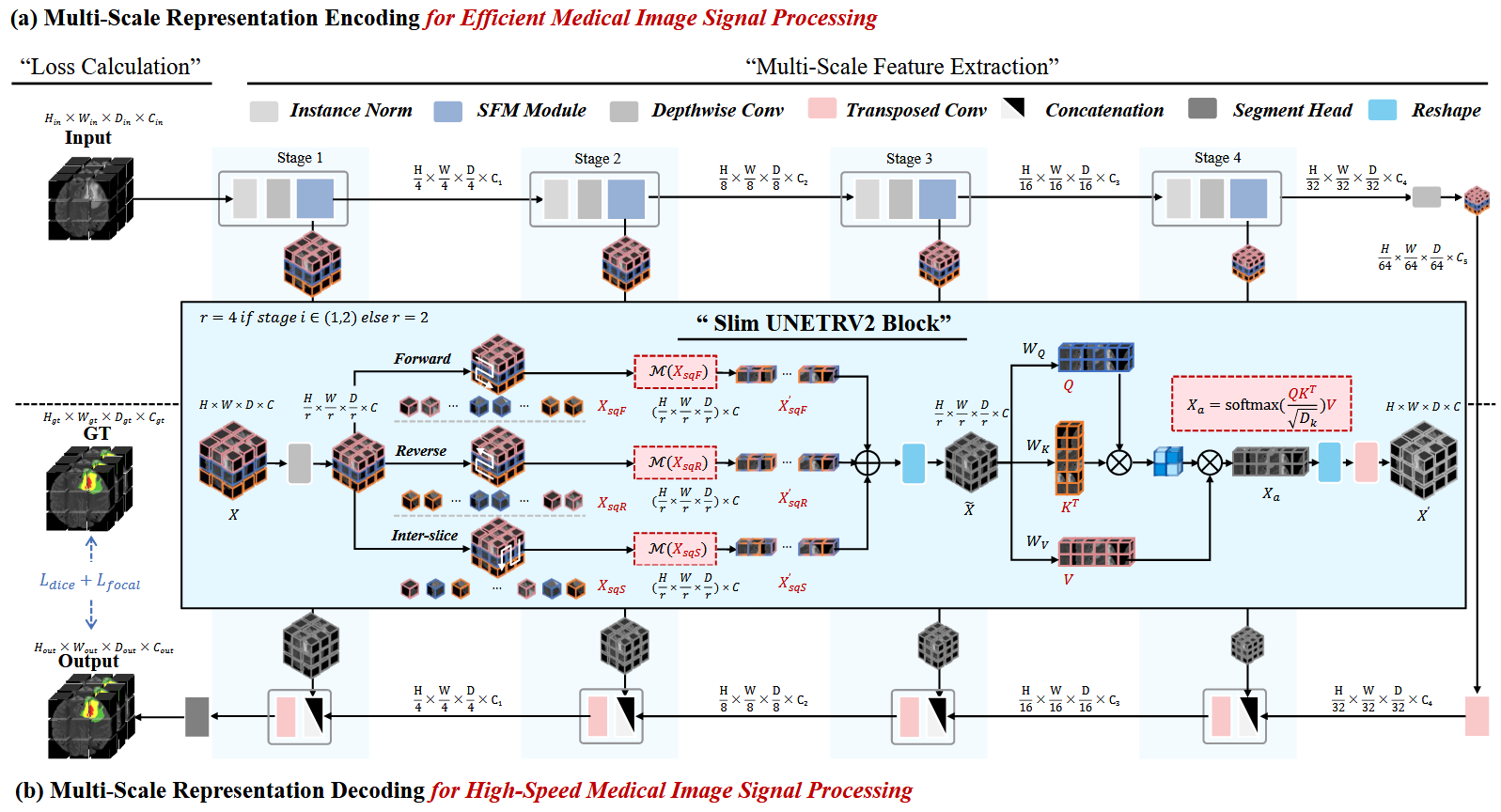
🎉New!!!🎉Slim UNETRV2: 3D Image Segmentation for Resource-Limited Medical Portable Devices
Yan Pang (Adviser), Jiaming Liang, Junming Yan, Ying Hu, Hao Chen, Qiong Wang*
Project Journal (JCR Q1, IF 9.8)
- This work introduces a novel lightweight 3D segmentation neural network, Slim UNETR-V2, which for the first time incorporates a sparse Tri-SSM computational mechanism, making it well-suited for deployment on resource-constrained clinical devices.
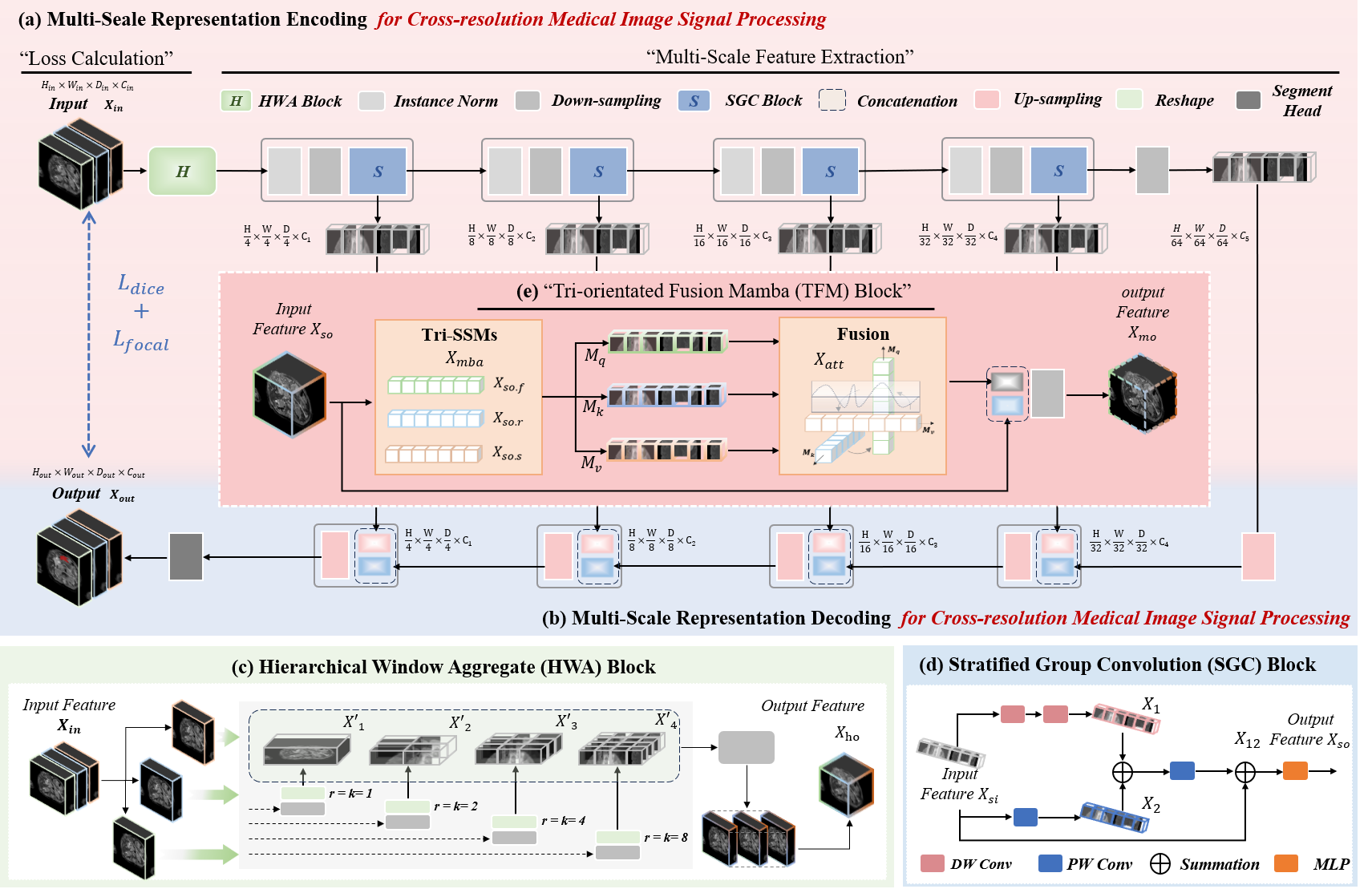
HWA-UNETR: Hierarchical Window Aggregate UNETR for 3D Multimodal Gastric Lesion Segmentation
Jiaming Liang, Lihuan Dai, Xiaoqi Sheng, Xiangguang Chen, Chun Yao, Guihua Tao, Qibin Leng, Hongmin Cai, Xi Zhong*
Project Conference paper (CCF-B)
- This work introduced the first multimodal MRI gastric tumor dataset GCM 2025, and its baseline model HWA-UNETR. This baseline model first proposed the tri-orientated fusion mamba mechanism to prioritize multimodal complex medical image analysis tasks.
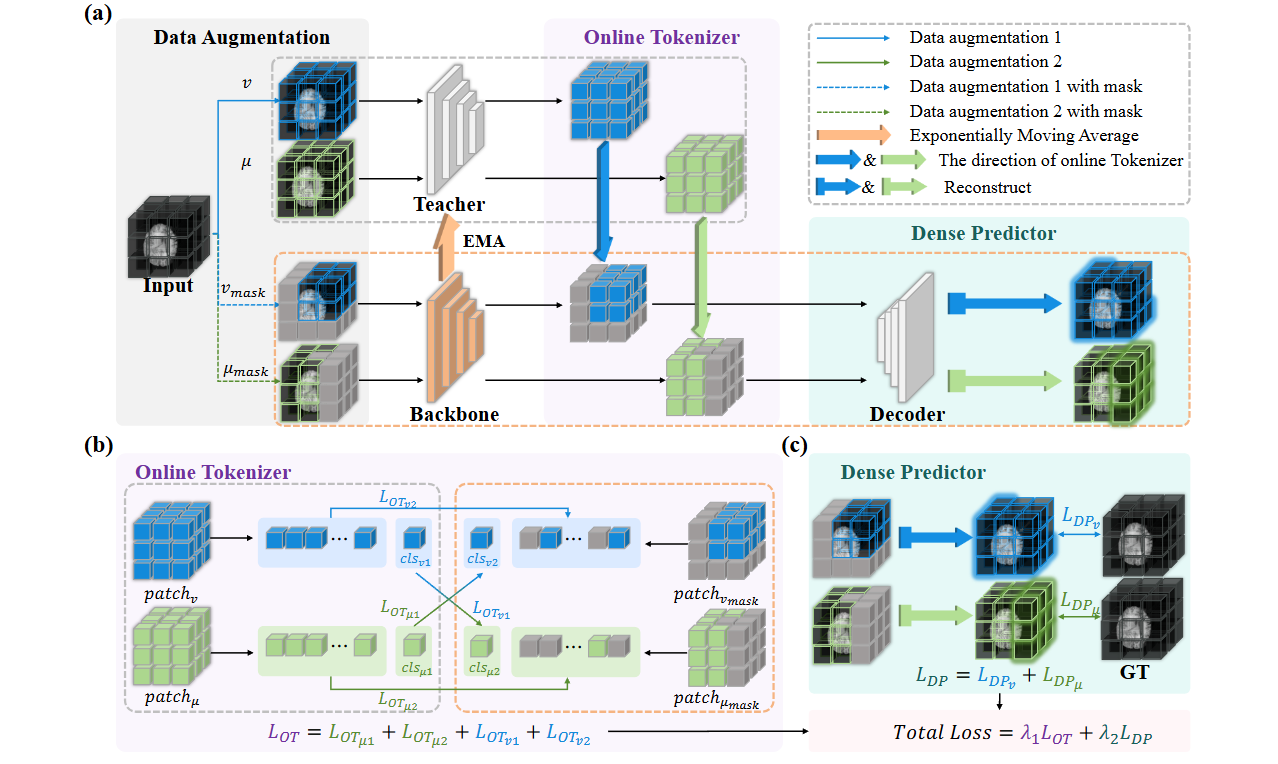
Online Self-distillation and Self-modeling for 3D Brain Tumor Segmentation
Yan Pang, Yunhao Li, Teng Huang*, Jiaming Liang, Zhen Wang, Changyu Dong, Dongyang Kuang, Ying Hu, Hao Chen, Tim Lei, Qiong Wang*
Project Journal (JCR Q1, IF 7.7)
- MOD is a plug-and-play component designed to enhance supervised learning models for brain tumor segmentation in data-scarce environments by integrating an Online Tokenizer and a Dense Predictor. These elements facilitate efficient representation learning through self-distillation and self-modeling on masked patches, promoting swift convergence.
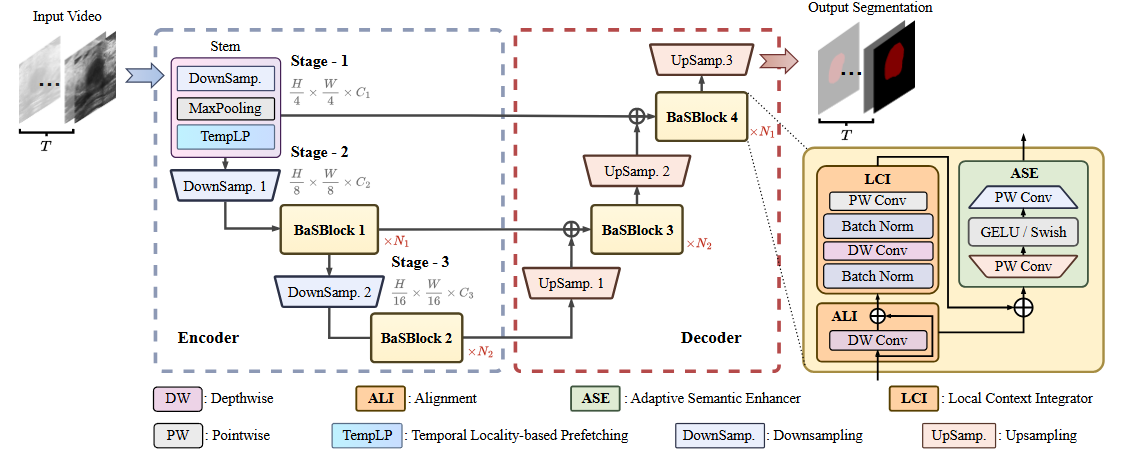
Efficient Breast Lesion Segmentation from Ultrasound Videos Across Multiple Source-limited Platforms
Yan Pang, Yunhao Li, Teng Huang*, Jiaming Liang, Ziyu Ding, Hao Chen, Baoliang Zhao, Ying Hu, Zheng Zhang, Qiong Wang*
Project Journal (JCR Q1, IF 7.7)
- BaS is an innovative, on-device breast lesion segmentation model designed for medical videos, integrating Stem module and BaSBlock to refine representations through inter- and intra-frame analysis, thus balancing segmentation performance and inference speed. This model surpasses existing top-performing models in efficiency and prediction accuracy on resource-limited devices by offering two versions, BaS-S for enhanced segmentation accuracy and BaS-L for faster inference times.
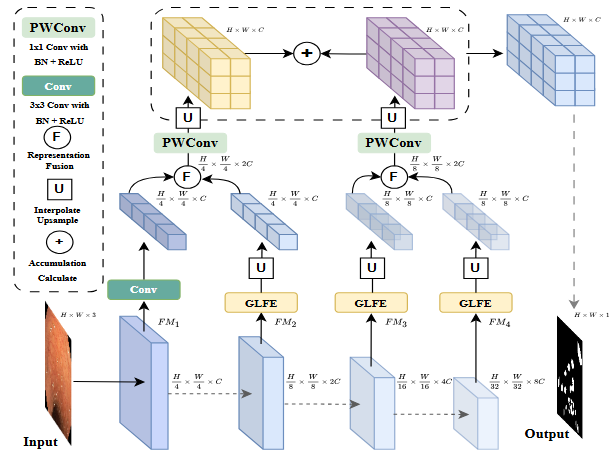
Jiaming Liang, Mingdu Zhang, Caiyan Tan, Teng Huang, Xi Zhang, Zheng Zhang*, Shegan Gao, Qian Sheng*, Yan Pang*
- CTIN, leveraging Transformer’s strengths and introducing a Global Local Fusion Extractor module, enhances the precision of endoscopic image segmentation by preserving boundary details and accurately localizing objects, thus demonstrating superior performance and robustness in challenging scenarios. This approach addresses the limitations of existing models in capturing complex boundaries and small objects, achieving state-of-the-art results on various metrics.

Teng Huang*, Weiqing Kong, Jiaming Liang, Ziyu Ding, Hui Li, Xi Zhang*
- LMS-GAT introduces a novel approach to human action recognition by facilitating information exchange through node concentration and diffusion across structural and temporal dimensions, selectively suppressing and reinstating structural node representations for specific actions ,and utilizing hierarchical shifted temporal windows to assess temporal information. This method effectively addresses dynamic changes during action transitions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in prediction accuracy on the NTU RGB+D 60 and 120 datasets, thus highlighting its improved efficacy in capturing and recognizing human actions.
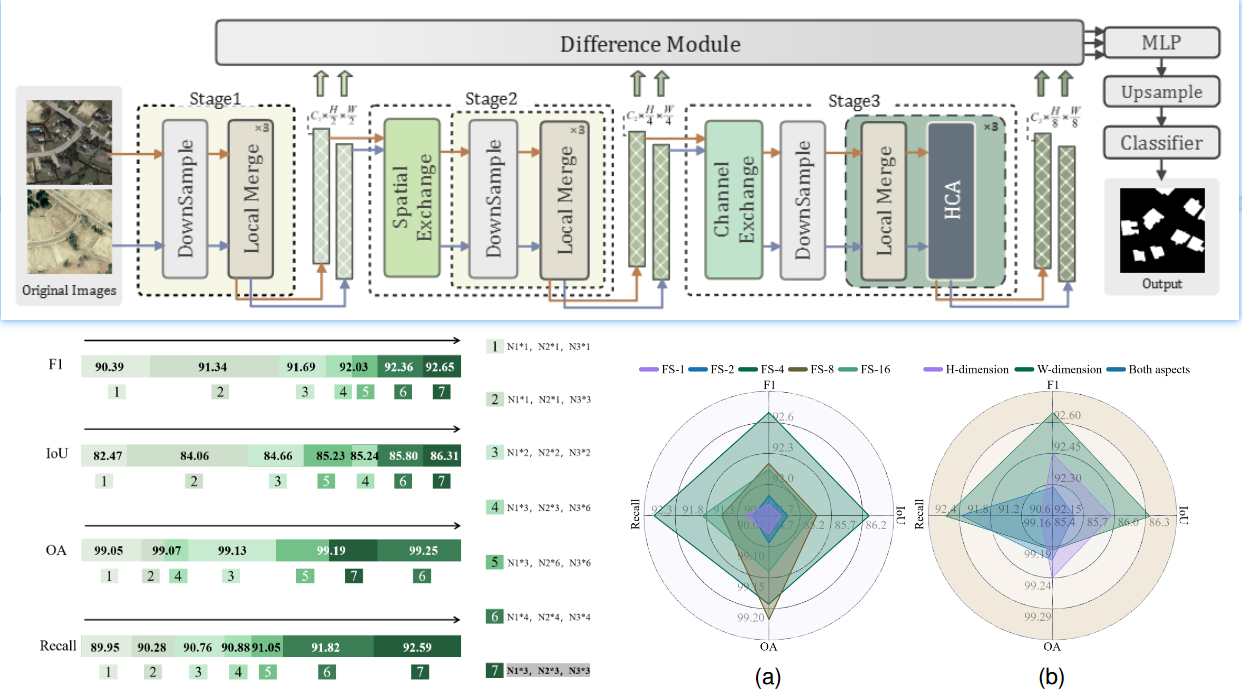
Teng Huang, Yile Hong, Yan Pang, Jiaming Liang, Jie Hong, Lin Huang, Yuan Zhang, Yan Jia, Patrizia Savi
Project Journal (JCR Q1, IF 5.6)
- AdaptFormer is designed to adaptively interpret hierarchical semantics in remote sensing change detection, employing tailored strategies across three semantic depths to enhance the identification of environmental changes, from straightforward operations for shallow semantics to cascaded depthwise attention for in-depth semantics. This approach enables AdaptFormer to surpass leading benchmarks, achieving exceptional F1 and IoU scores of 92.65% and 86.31% on the LEVIR-CD dataset, and 97.59% and 95.29% on the DSIFN-CD dataset, respectively.
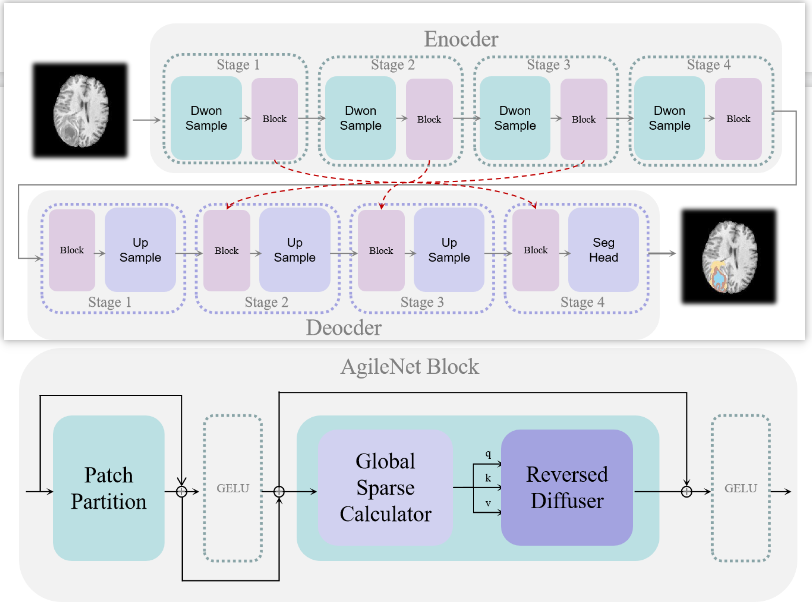
AgileNet: A Rapid and Efficient Breast Lesion Segmentation Method for Medical Image Analysis
Jiaming Liang, Teng Huang*, Dan Li, Ziyu Ding, Yunhao Li, Lin Huang, Qiong Wang, Xi Zhang*
- AgileNet is an efficient lesion segmentation model that balances accuracy and efficiency by combining the strengths of convolutional neural networks and transformers, utilizing an Agile block for cost-effective information exchange that incorporates both global and local contexts. Demonstrating superior performance in terms of accuracy, model size, and throughput on resource-constrained devices, AgileNet offers a promising solution for accurate and efficient medical image segmentation in such settings.
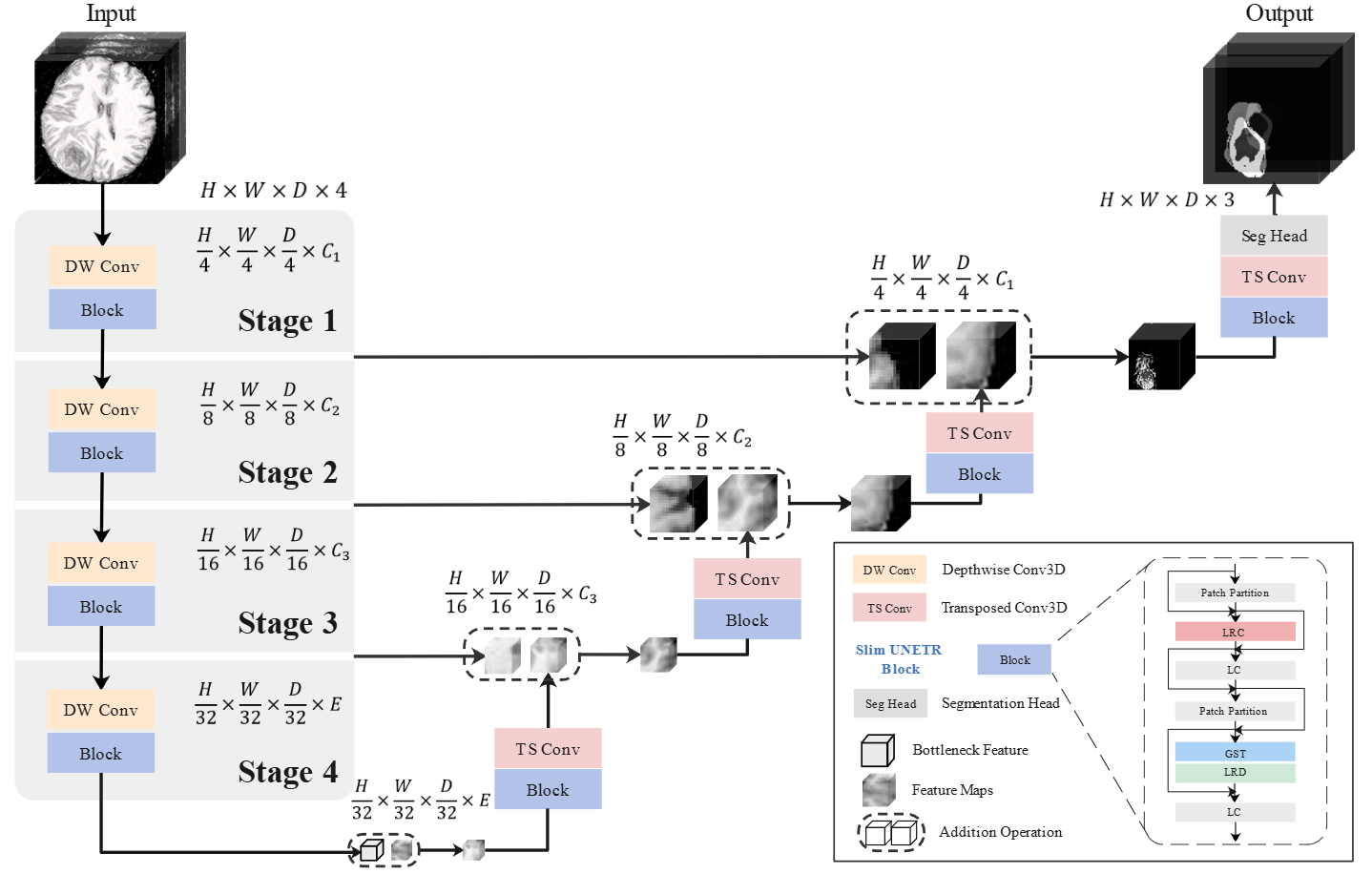
Yan Pang (Adviser), Jiaming Liang, Teng Huang*, Hao Chen, Yunhao Li, Dan Li, Lin Huang, Qiong Wang*
Project Journal (JCR Q1, IF 9.8)
- SlimUNETR is a lightweight 3D medical image segmentation model that achieves state-of-the-art performance on the BraTS2021 and other 3D lesion segmentation datasets, while also seeing a significant reduction in the number of parameters and floating-point computations.
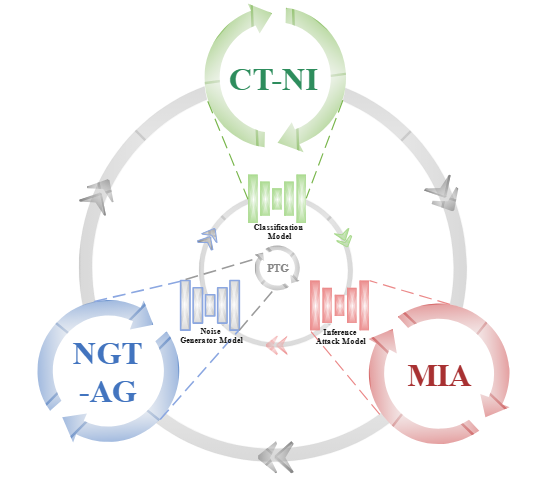
GanNoise: Defending against black-box membership inference attacks by countering noise generation
Jiaming Liang, Teng Huang*, Zidan Luo, Dan Li, Yunhao Li, Ziyu Ding
- GanNoise is a novel training framework designed to preserve privacy in deep learning models by generating noise that adds randomness to private data during training, thereby preventing excessive memorization of the actual training data while maintaining classification accuracy. This approach effectively defends against membership inference attacks without compromising model performance, outperforming existing advanced MIA defense solutions in terms of efficiency across various datasets.
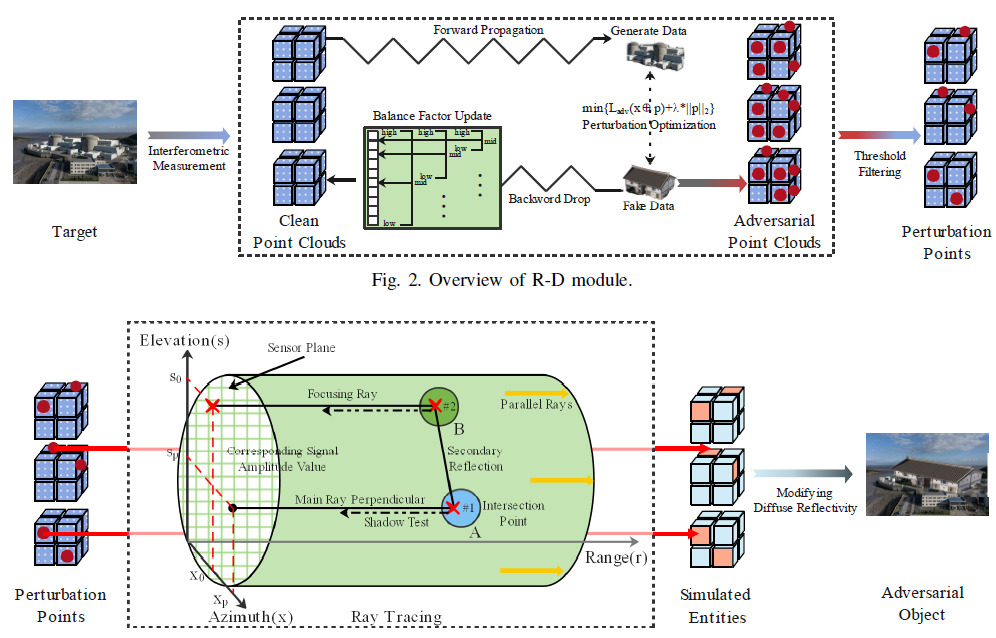
Bo Wei, Teng Huang*, Xi Zhang, Jiaming Liang, Yunhao Li, Ziyu Ding, Cong Cao, Dan Li, Yongfeng Chen, Huagang Xiong, Feng Jiang, Xiqiu Zhang*
- This article explores the increased privacy risks associated with multi-task learning (MTL) compared to traditional single-task learning, through the design of model extraction attacks (MEA) and membership inference attacks (MIA) in MTL. Evaluations across six MTL model architectures and two popular MTL datasets reveal that both the number of tasks and the complexity of training data significantly influence attack performance, demonstrating that MTL is more vulnerable to these attacks than single-task learning. This highlights the need for enhanced privacy measures in MTL frameworks.
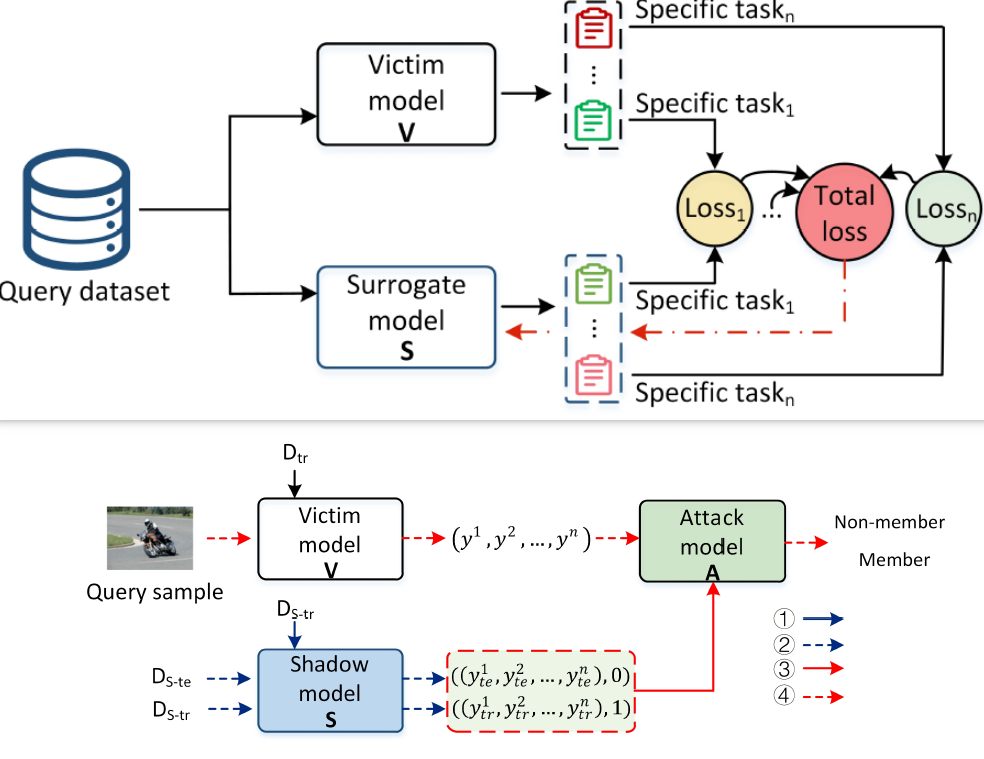
MTL-Leak: Privacy Risk Assessment in Multi-Task Learning
Hongyang Yan, Anli Yan, Li Hu, Jiaming Liang, Haibo Hu*
- Multi-task learning (MTL) supports simultaneous training over multiple related tasks and learns the shared representation. While improving the generalization ability of training on a single task, MTL has higher privacy risk than traditional single-task learning because more sensitive information is extracted and learned in a correlated manner. Unfortunately, very few works have attempted to address the privacy risks posed by MTL. In this article, we first investigate such risk by designing model extraction attack (MEA) and membership inference attack (MIA) in MTL. Then we evaluate the privacy risks on six MTL model architectures and two popular MTL datasets, whose results show that both the number of tasks and the complexity of training data play an important role in the attack performance. Our investigation shows that MTL is more vulnerable than traditional single-task learning under both attacks.
